Evaluation data creation tutorial¶
Overview¶
For the evaluation of RAGs we need data, but in most cases we have little or no satisfactory data.
However, since the advent of LLM, creating synthetic data has become one of the good solutions to this problem.
The following guide covers how to use LLM to create data in a form that AutoRAG can use.
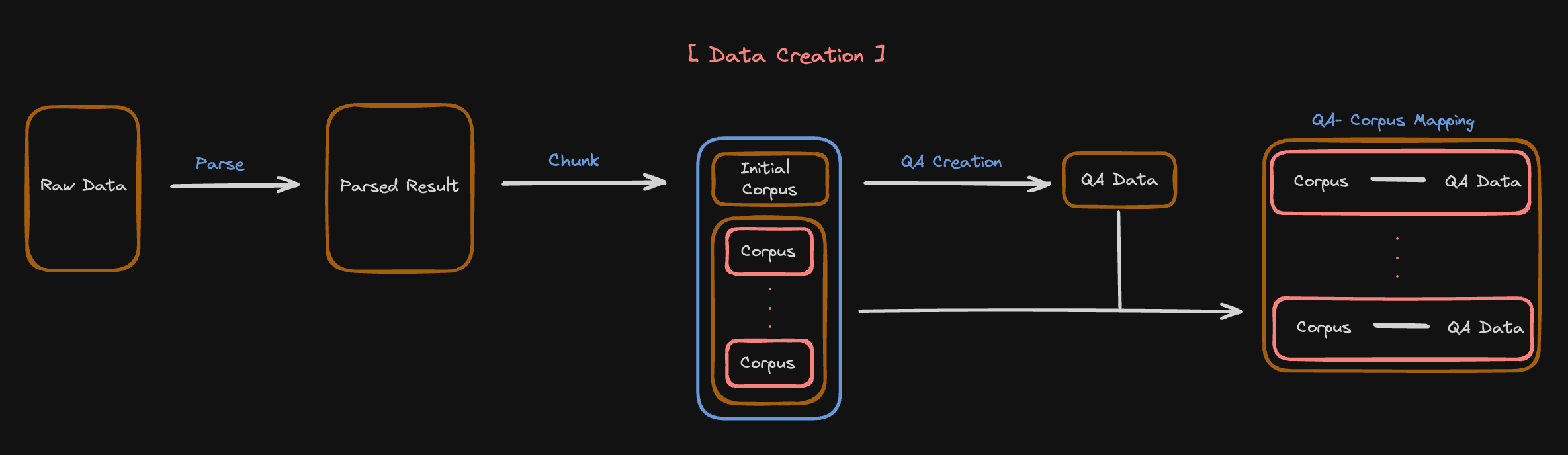
1. Parse¶
You can make different parsing results from the raw data using the parsing YAML file. The sample parsing YAML file looks like this.
modules:
- module_type: langchain_parse
parse_method: [pdfminer, pdfplumber]
With this YAML file, you can get the parsed data with pdfminer and pdfplumber.
You can execute this parsing YAML file by using the following code.
from autorag.parser import Parser
filepaths = "./data/*.pdf"
parser = Parser(filepaths, "./parse_project_dir")
parser.start_parsing("./parsing.yaml")
Then you can check out the parsing result in the ./parse_project_dir directory.
For more details about parsing, please refer here.
2. QA Creation¶
From the parsed results, you can select the best parsed data for AutoRAG. After you selected, you can create QA data for the AutoRAG.
The example is shown below, the initial_raw_df is selected raw data.
from llama_index.llms.openai import OpenAI
from autorag.data.beta.filter.dontknow import dontknow_filter_rule_based
from autorag.data.beta.generation_gt.llama_index_gen_gt import (
make_basic_gen_gt,
make_concise_gen_gt,
)
from autorag.data.beta.query.llama_gen_query import factoid_query_gen
from autorag.data.beta.sample import random_single_hop
from autorag.data.beta.schema import Raw
initial_raw = Raw(initial_raw_df)
initial_corpus = initial_raw.chunk(
"llama_index_chunk", chunk_method="token", chunk_size=128, chunk_overlap=5
)
llm = OpenAI()
initial_qa = (
initial_corpus.sample(random_single_hop, n=3)
.map(
lambda df: df.reset_index(drop=True),
)
.make_retrieval_gt_contents()
.batch_apply(
factoid_query_gen,
llm=llm,
)
.batch_apply(
make_basic_gen_gt,
llm=llm,
)
.batch_apply(
make_concise_gen_gt,
llm=llm,
)
.filter(
dontknow_filter_rule_based,
lang="en",
)
)
initial_qa.to_parquet("./initial_qa.parquet", "./initial_corpus.parquet")
We recommend you find the optimal pipeline first from this initial data. Check out here to see the optimization tutorial.
3. Chunking Optimization¶
After finding the initial optimal pipeline, this time you are to optimize the chunking method. First, you can create various chunking results from the parsed data.
The chunking YAML file looks like this.
modules:
- module_type: llama_index_chunk
chunk_method: [ Token, Sentence ]
chunk_size: [ 1024, 512 ]
chunk_overlap: 24
add_file_name: english
- module_type: llama_index_chunk
chunk_method: [ SentenceWindow ]
sentence_splitter: kiwi
window_size: 3
add_file_name: english
With this YAML file, you can get the chunked data with Token, Sentence, and SentenceWindow with different chunk sizes.
You can execute this chunking YAML file by using the following code.
from autorag.chunker import Chunker
chunker = Chunker.from_parquet("./initial_raw.parquet", "./chunk_project_dir")
chunker.start_chunking("./chunking.yaml")
Then you can check out the chunking result in the ./chunk_project_dir directory.
For more details about chunking, please refer here.
4. QA - Corpus mapping¶
For the chunking optimization, you can evaluate RAG performance with different corpus data. You already have the optimal pipeline from the initial QA data, so you can use this pipeline to evaluate the RAG performance with different corpus data.
Before that, you must update all qa data with the new corpus data.
It uses update_corpus method.
It is highly recommending you to keep the initial QA instance.
If not, you need to build QA instance again from the initial raw (parsed) data and corpus data.
from autorag.data.beta.schema import Raw, Corpus, QA
raw = Raw(initial_raw_df)
corpus = Corpus(initial_corpus_df, raw)
qa = QA(initial_qa_df, corpus)
new_qa = qa.update_corpus(Corpus(new_corpus_df, raw))
Now new_qa have new retrieval_gt data for the new corpus.
Now with the new corpus data and new qa datas, you can evaluate the RAG performance with different corpus data.